
Sudocrem® for Eczema
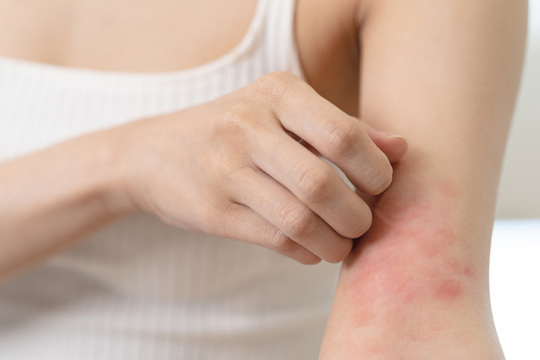
If you have eczema then you are all too familiar with dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It can appear on your face, neck, and the insides of elbows and knees, and can be caused by genetics and allergens, environmental factors, or even stress. It’s important to find what works best for you to help keep your skin comfortable and healthy. But is Sudocrem® good for eczema? The quick answer is “Yes!” and here’s why.
How Sudocrem® Antiseptic Healing Cream helps eczema:

- Treats inflamed skin
- Soothes irritated skin helping to alleviate the need to itch
- Reduces redness
- Supports the skin’s natural healing process
- Shields eczema-prone skin against triggers that might worsen flare-ups
How to use Sudocrem® on eczema:
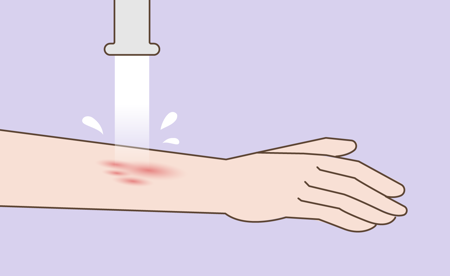
1. Clean
Gently cleanse the affected area with lukewarm water and pat dry
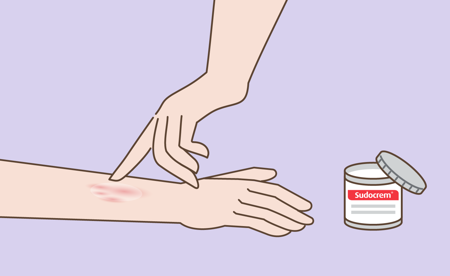
2. Apply
Spread a thin layer of Sudocrem® over the affected area
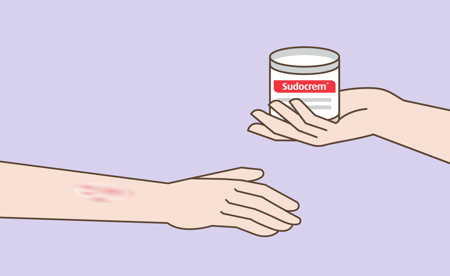
3. Repeat
Use Sudocrem® as often as needed.






